The Hong Kong Financial Authority (HKMA), with analytical assist from Deloitte, has launched its e-HKD Pilot Programme Section 2 Report, providing a glance into how central financial institution digital currencies (CBDCs) and different digital cash kinds might reshape the town’s monetary ecosystem.
The report reveals a pivotal transition — from bodily money to digital cash powered by distributed ledger know-how (DLT) — and descriptions how Hong Kong is positioning itself as a world chief in digital finance, tokenisation, and next-generation funds infrastructure.
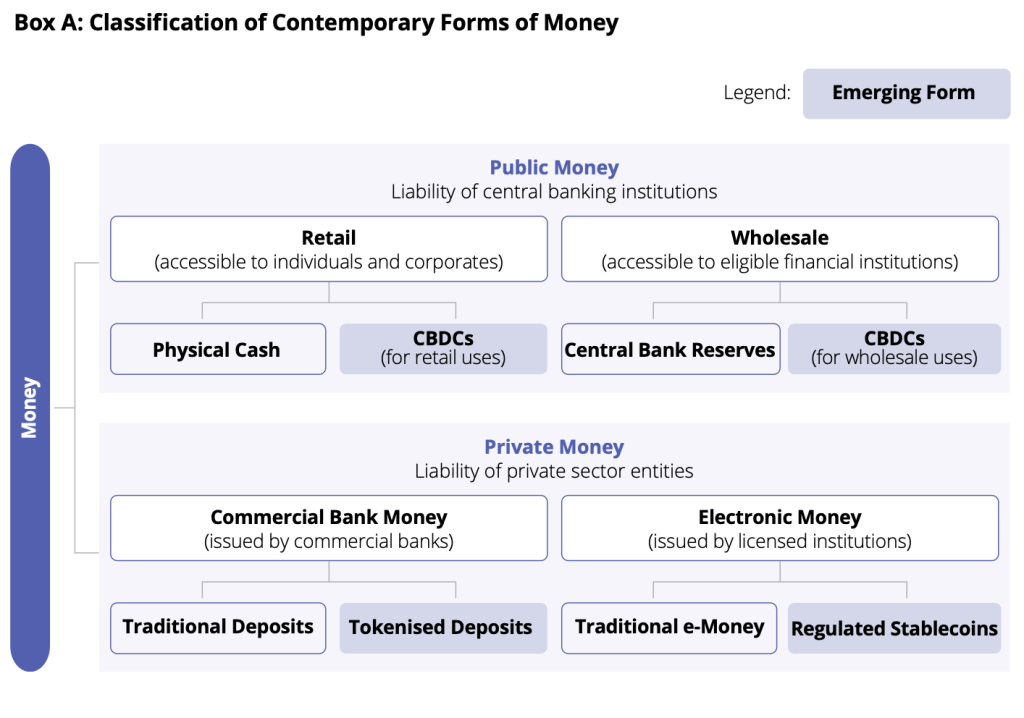
Increasing the Digital Cash Panorama
In response to the HKMA report, the digital cash panorama is evolving into two important classes: public cash and personal cash. Public cash contains central financial institution digital currencies just like the e-HKD, whereas personal cash encompasses tokenised deposits and controlled stablecoins.
These improvements are constructing the inspiration for tokenisation in Hong Kong, enabling quicker, extra clear, and programmable transactions that join conventional finance with the rising Web3 ecosystem.
The HKMA has been researching the e-HKD since 2017, conducting pilot research and technical experiments to discover its potential in each wholesale and retail settings.
With Section 2, the main focus broadened to incorporate comparisons between the e-HKD and personal types of digital cash, evaluating their usability, scalability, and industrial viability.
Key Themes and Findings
The Section 2 pilots, performed with 11 business companions throughout the banking, funds, and know-how sectors, explored three central themes:
Settlement of Tokenised Property: Pilots examined using a hypothetical e-HKD for atomic settlement of tokenised belongings akin to cash market funds and bonds.
Outcomes confirmed that DLT-based settlement might shorten cycles from T+2 to T+0, enhancing liquidity and lowering counterparty danger. Nonetheless, banks indicated that tokenised deposits may provide comparable effectivity with fewer infrastructure adjustments.
Programmability: The report examined the potential of programmable funds utilizing good contracts and purpose-bound cash (PBM). Pilot use instances included inexperienced reward vouchers, escrow-based prepayments, and provide chain financing.
Whereas programmability enhances automation and transparency, the HKMA discovered that industrial adoption fashions stay restricted, with no clear enterprise case for large-scale rollout.
Offline Funds; Offline e-HKD pilots explored Tremendous SIM and NFC-based funds that function with out web connectivity. Given Hong Kong’s strong digital infrastructure and current offline cost programs, the HKMA concluded that an offline e-HKD would possible add restricted incremental profit at current.
The Street Forward
The HKMA, supported by Deloitte’s evaluation, will prioritise wholesale use instances for the e-HKD, significantly within the settlement of tokenised belongings and interbank transactions.
The central financial institution will proceed to evaluate retail purposes whereas laying the coverage, authorized, and technical groundwork to make sure readiness by 2026.
As the worldwide race towards digital cash intensifies, Hong Kong’s collaborative strategy — combining public oversight with personal innovation — positions it on the forefront of monetary transformation. The e-HKD initiative displays not simply the town’s dedication to technological development, but additionally its strategic function in shaping the subsequent period of cash — related, environment friendly, and inclusive.
The put up Hong Kong Advances Digital Cash Technique as HKMA’s e-HKD Pilot Programme Enters Section Two appeared first on Cryptonews.